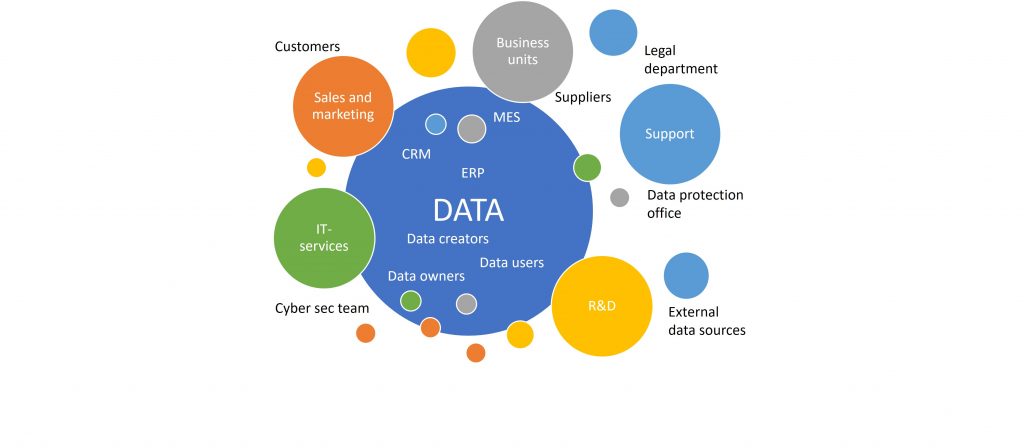
It can be surprising to realize the number of stakeholders that use, create, and own the data in the company. Stakeholders and their concerns need to be addressed from the start to finish if one aims to utilize data across the company’s silos.
When you want to conduct analysis beyond typical sales or revenue forecasts, such as AI-based analysis, requirements for data sources increases. For example, in the use cases presented in Part I of this blog series (e.g., tailored products), analysis is only possible when one has access to several databases in company, such as CRM, ERP, and IT Service Management (ITSM) systems.
In each of these systems, there are several stakeholders involved—whether they are the data owners, those who create or use the data, or even those who maintain the IT system that holds the data (see Figure 1 and 2).
The current blog (Part II) explores roles of data stakeholders in AI-driven sales. In the blog serie, we have previously discussed about use cases (Part I), whilst upcoming blogs will tackle data wrangling (Part III), confidentiality of AI model (Part IV) and business benefit (Part V). Blogs are published at https://www.innosale.eu/. Please also join our webinar 29.5.2024 14:00-15:30 Finnish time (13:00-14:40 CET), registration link.